筆記 covariance matrix $R$ 的 determinant 意義以及他的 bound. 這是在讀 Time-delay estimation via linear interpolation and cross correlation 時的 appendix 證明. 覺得有用就筆記下來.
開門見山, $det(R)$ 可以想成 volumn (等於所有 eigenvalues 相乘), 然後 upper bound 就是所有對角項元素相乘.
$$\begin{align} det(R)=\prod_i \lambda_i \leq \prod_i r_{ii} \end{align}$$$\lambda_i$ 是 i-th eingenvalue.
事實上只要 $R$ 是 square matrix, 則 $|det(R)|$ 等於用每個 row vector 做出來的 “平行六面體” 的體積 [ref]
以下筆記論文中證明 $det(R)$ 的 upper bound, 從這個 bound 我們也能看出物理意義.
Upper bound of the determinant of positive definite matrix
[Theorem]: 令 $H$ 為 $L$ by $L$ 正定矩陣, 則
$$\begin{align}
det(H) \leq \prod_{i=1}^{L} h_{ii}
\end{align}$$
[Proof]:
先將 $H$ 作如下拆解
$$\begin{align}
H=\left( \begin{array}{cc} \tilde{H} & h \\
h^T & h_{LL} \end{array} \right)
\end{align}$$ 其中 $\tilde{H}$ 是 $L-1$ by $L-1$ 矩陣.
從 Determinant of block matrices 我們知道:
$$\begin{align}
det(H)=det(\tilde{H})(h_{LL}-h^T \tilde{H}^{-1}h)
\end{align}$$ 因為 $H$ 是正定, 所以 $\tilde{H}$ 也是正定, 包含其 inverse
Every principal submatrix of a positive definite matrix is positive definite.
正定的 $det>0$, 以及正定的二次式 $>0$, 帶入到 (4) 就不難發現
$$\begin{align}
det(H)\leq h_{LL}det(\tilde{H})
\end{align}$$ 重複此步驟就能推導出 (2)
Determinant of covariance matrix
我們知道 covariance matrix $R$ 是正定 (嚴格上為半正定, 如果沒有兩個完全 linear depedent 的維度的話, 就是正定), 因此符合 upper bound (2).
觀察當 coordinate 之間為 independent 時, 表示非對角項都是 $0$, 只剩下對角項 (每個維度的 variance). 這時 (2) 的不等式變成等式, 對角項相乘意義相當於算 volumn
可以看出兩點結論
- covariance matrix 對角項的相乘總是會比 $det$ 大
- coordinate 之間是 independent 則 covariance matrix 對角項的相乘會等於 $det$
Correlation matrix
我們知道 correlation matrix 對角項都是 $1$, 且是正定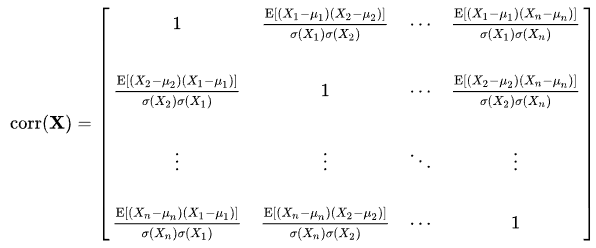
根據以上的討論知道:
$$\begin{align}
0\leq det(\mbox{corr}(X))\leq 1
\end{align}$$
Take Home Messages
令 $R$ 為 covariance matrix, $\tilde{R}$ 是 correlation matrix
- $R$ 對角項的相乘總是會比 $det(R)$ 大
- coordinate 之間是 independent 則 $R$ 對角項的相乘等於 $det(R)$
- $det(\tilde{R})$ 在 0 和 1 之間 (包含)
令 $A$ 為 square matrix, 則 $|det(A)|$ 等於以每個 row vector 做出來的 “平行六面體” 的體積 [ref]